Create a router
A router can be created in two ways:- Manually on the Routers page as documented in the following section.
- After you create a network, a new router is automatically created in the cloud to enable traffic routing. You can configure automatically created routers using the same settings available for manually created routers.
Create a router manually
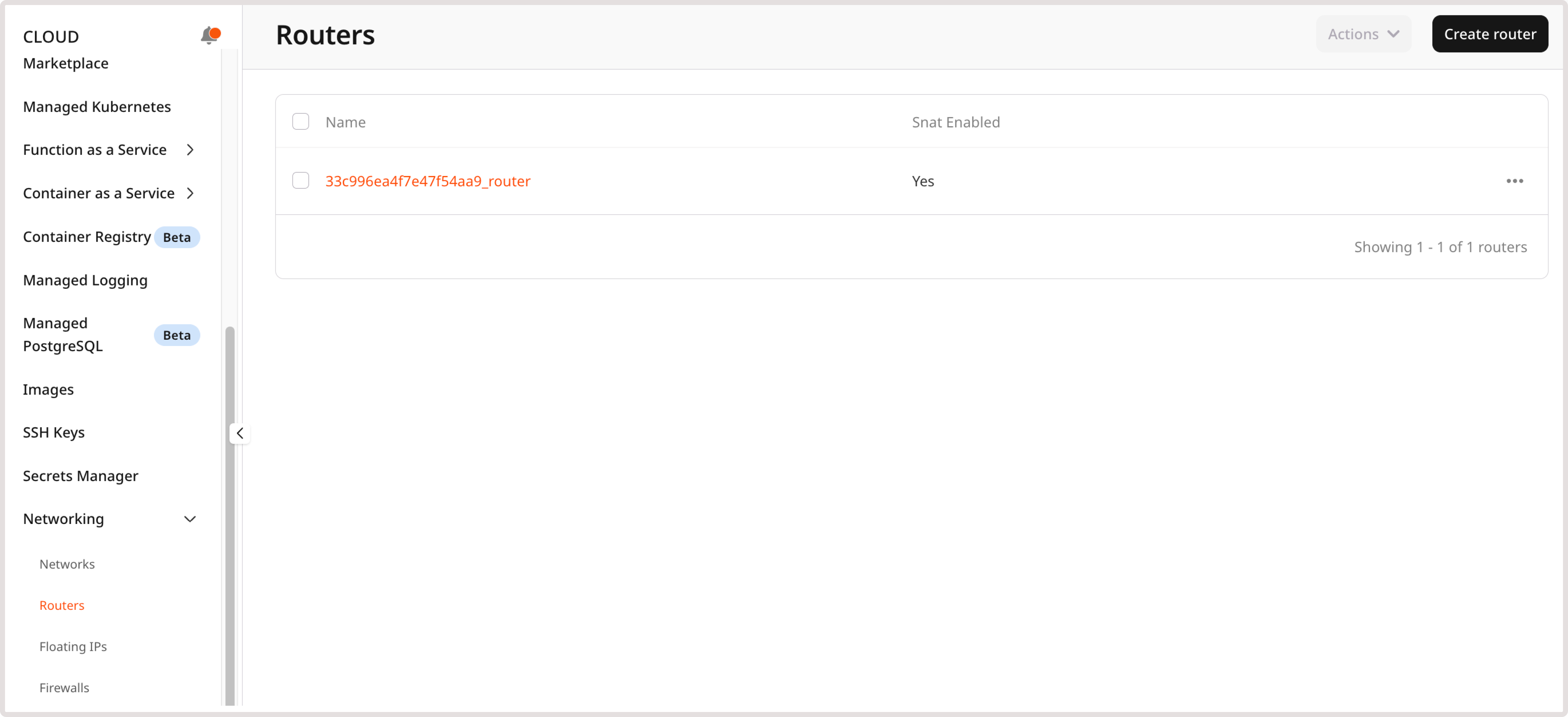
1. In the Gcore Customer Portal, navigate to Cloud > Networking. 2. Go to the Routers page and click Create router.
Router control and route tables
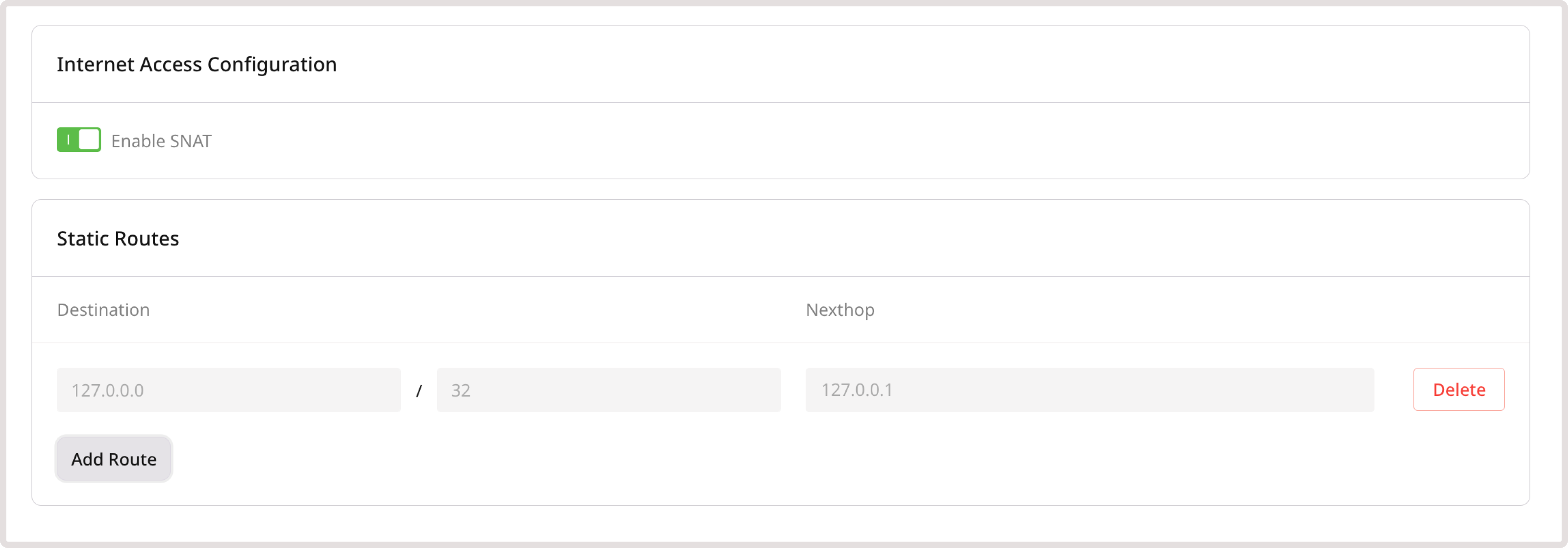
Routing is based on route tables, which define the paths that network traffic takes from a VM to other destinations. These destinations can be inside or outside the private network. The tables contain static routes, which consist of a target subnet prefix in CIDR notation and the nexthop’s internal IP address (the virtual machine or router handling the traffic). A router is automatically created when a network is created, but customers can also create and configure routers manually. By default, all routers have SNAT (Source Network Address Translation) enabled, allowing instances in a private network to access the external network. Customers can add subnets to a router and define static routes for controlling traffic flow.Manage routers
To manage routers: 1. Open the Routers page in the Gcore Customer Portal. 2. Click the router name to access its settings. Alternatively, click the three-dot icon next to the router you want to manage and then select Overview.
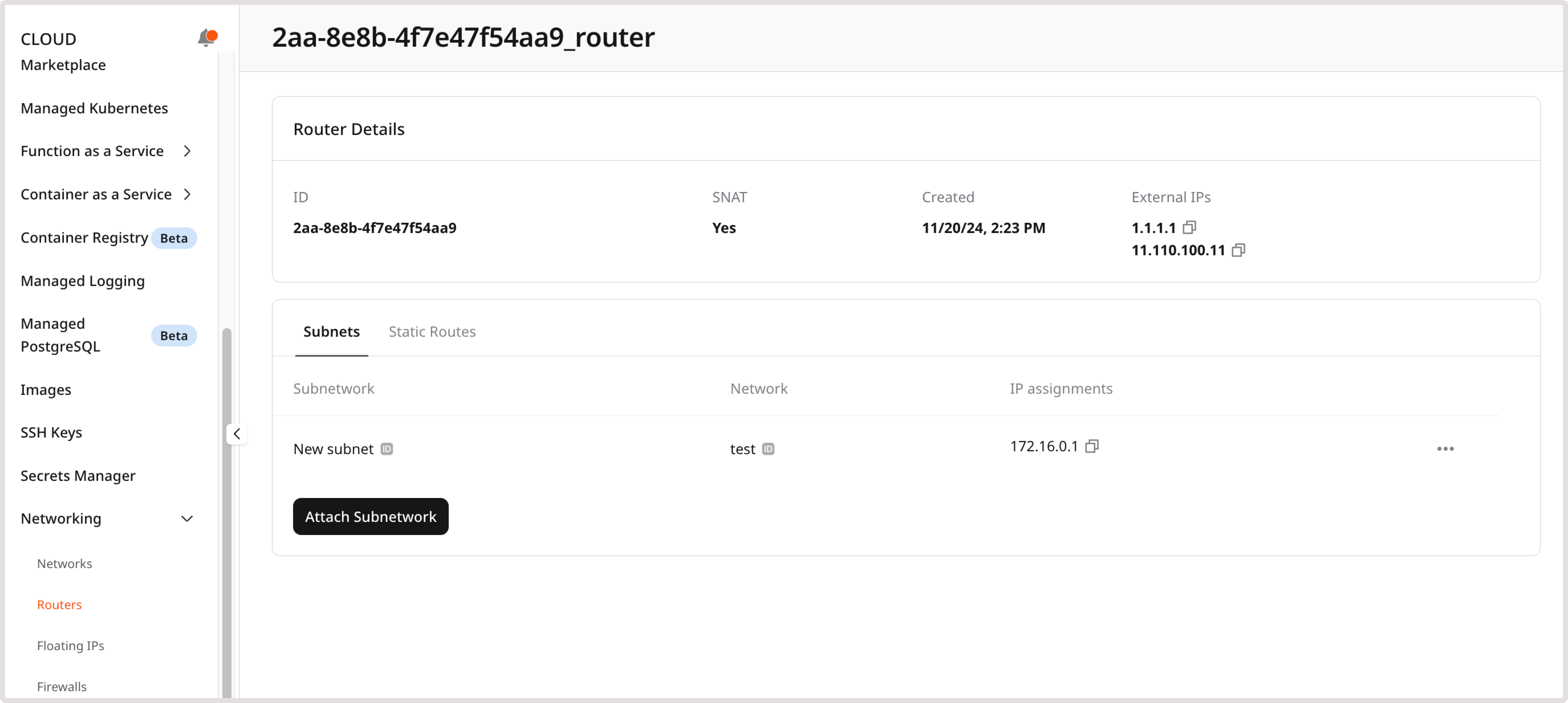
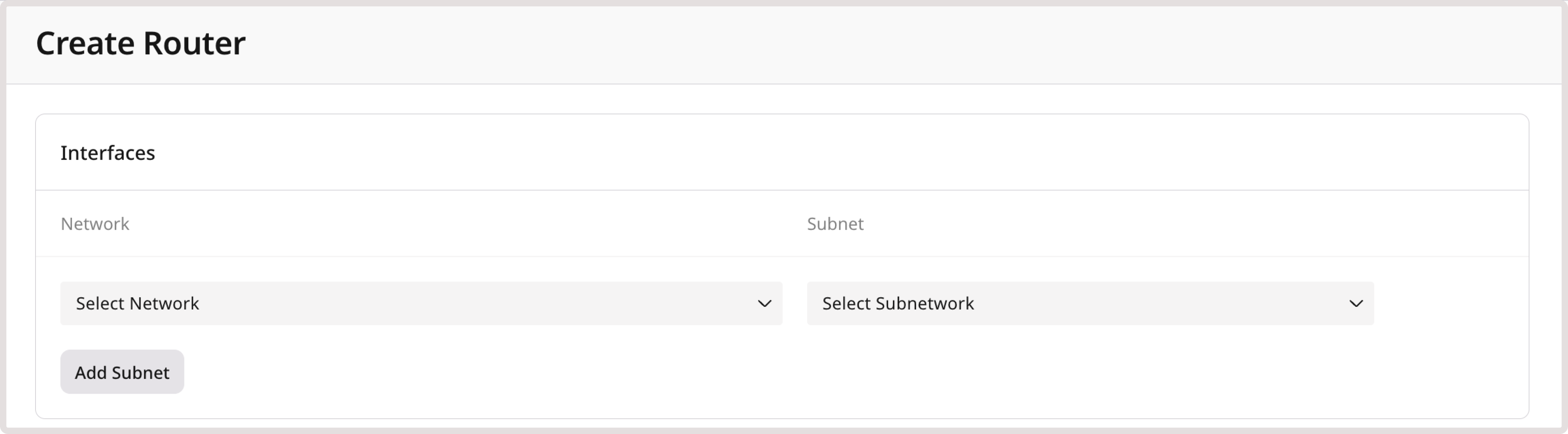
Configure a subnetwork
In the Subnets section, you can manage the list of subnets added to the router, add new subnets, and delete the existing ones. When creating a subnetwork, pay attention to the supported CIDR ranges:- 10.0.0.0/8
- 172.16.0.0/12
- 192.168.0.0/16
- fc00::/7
WarningThe specified CIDR ranges must align with the destinations configured in your static routes.
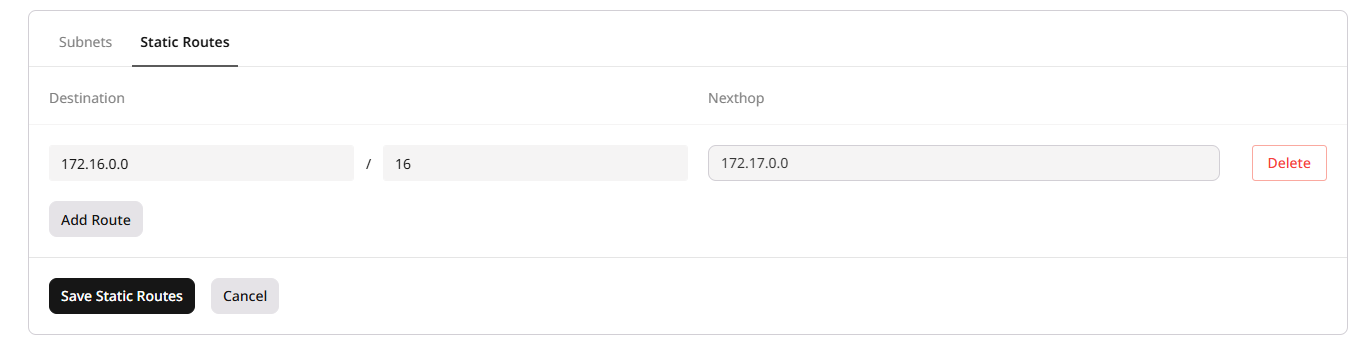
Configure static routes
There are two types of static routes: host routes (Layer 2) for internal subnet routing and router static routes (Layer 3) for inter-network traffic control.Host routes for subnets (Layer 2)
Host routes operate at Layer 2 without relying on a router, controlling traffic flow within a subnet. They are assigned to instances through DHCP or cloud-init instead of being distributed by a router. DHCP dynamically assigns host routes based on network configurations, while cloud-init configures them automatically at instance startup using predefined settings. Host routes are automatically assigned to instances within the same subnet and do not require manual configuration. They are not advertised beyond the subnet, ensuring traffic stays internal.Router static routes (Layer 3)
Router-level static routes operate at Layer 3 and require a router to forward traffic between networks. These routes are distributed to instances using Router Advertisement. When a router is present, it announces available routes to connected instances. To configure a static route: 1. Go to the Routers page in the Gcore Customer Portal. 2. Open the settings of the desired router. 3. Open the Static Routes tab. 4. Click Edit Static Routes → Add Route.