- API Privileged Access
- API Admin Access
- Indicate API Privileged User
- Indicate API Admin User
- Ignore Email Address Detection
- Ignore Phone Number Detection
- Auth Endpoint
- Ignore CCN Detection
- Ignore SSN Detection
Configure API protection
The following steps will guide you through the process of protecting your endpoints from unauthorized access. After you complete the steps, it’s important to enable the relevant policies within the Advanced API protection policy group to make sure everything is set up correctly.InfoTo ensure that your APIs are fully protected, enable the API Discovery feature or manually add your endpoints to the API base path so that WAAP correctly recognizes these endpoints as associated with your domain.
Step 1. Group endpoints based on their access levels
The first step in API protection is to categorize your endpoints based on their authorization levels:- Admin : Endpoints that can only be accessed by admin users.
- Privileged : Endpoints that can be accessed by privileged users and admins.
- Non-privileged : Endpoints accessible to users with no permissions.
- API Privileged Access : This tag grants permission to reach any privileged API endpoint.
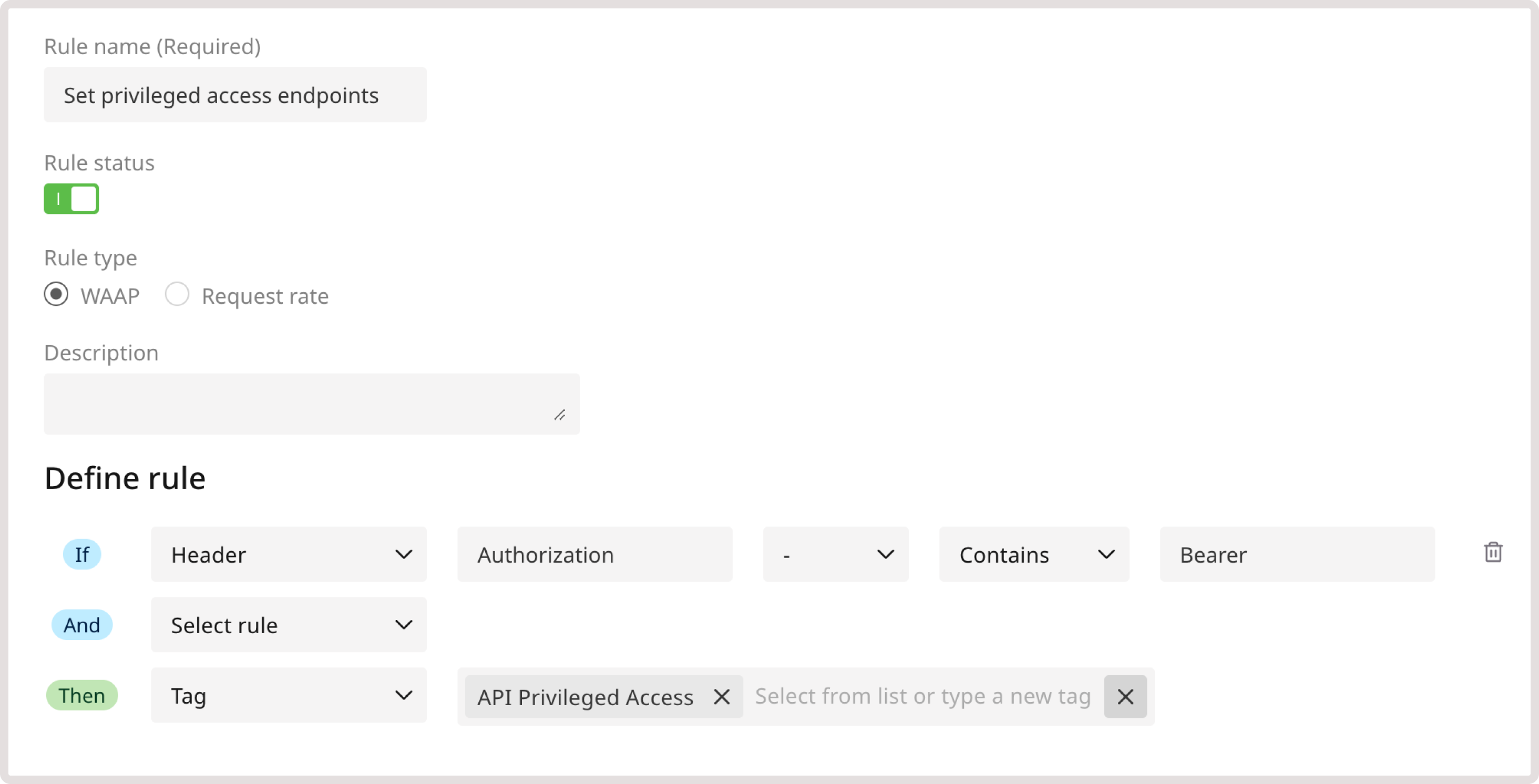
- API Admin Access : This tag allows interaction with all API endpoints. In the current rule example, choose this tag.
Step 2. Define user roles that can access endpoints
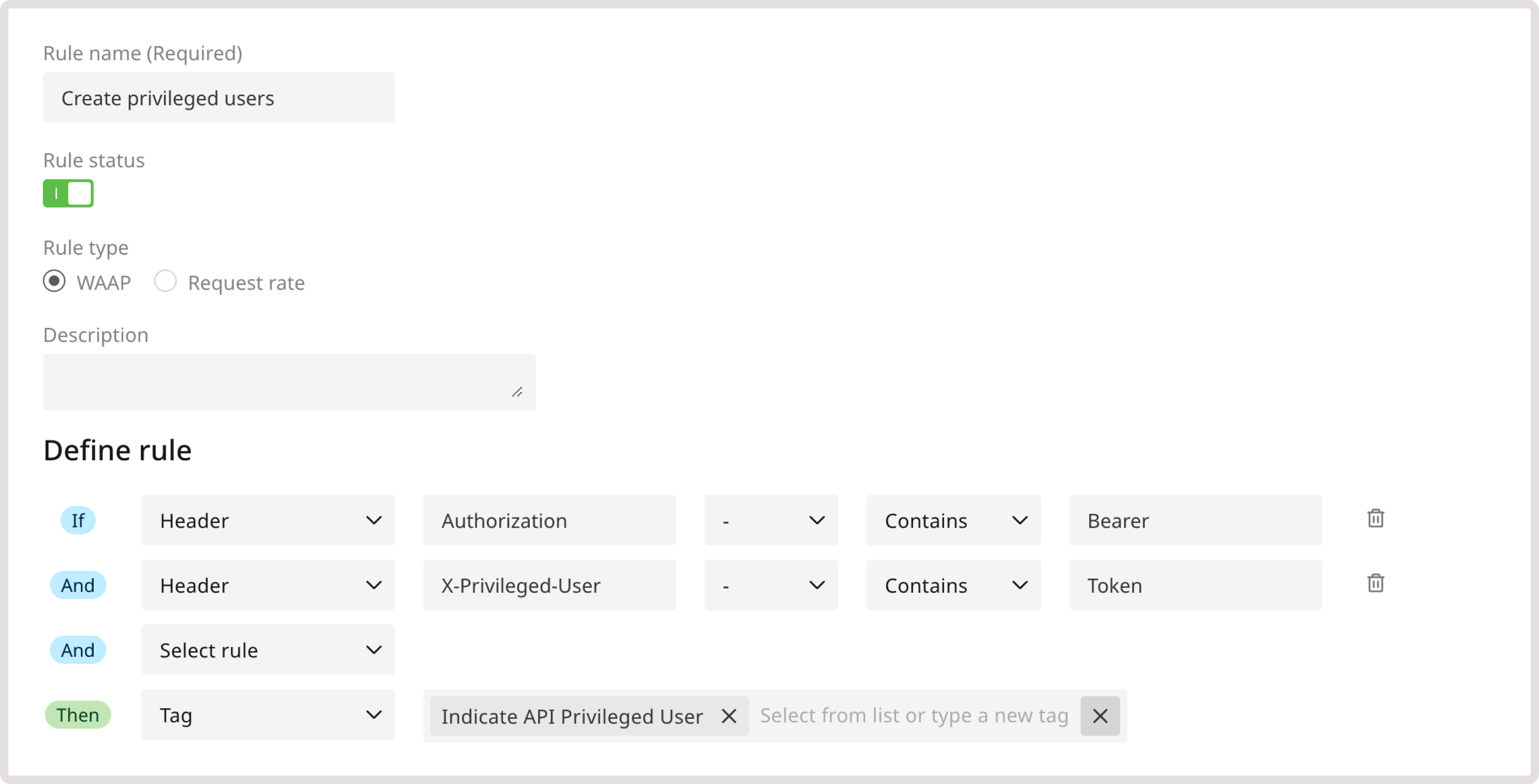
After you define access levels for API endpoints, you need to configure which users can interact with those endpoints. To do so, create a new custom rule for each user type. For example, create a rule that identifies a request as coming from an admin user if the request contains a valid bearer token in the authorization header.TipIt’s a good practice to add multiple conditions to custom rules. Complex rules are harder to bypass and more nuanced, which reduces the probability of false positives.
- In the IF section, select Header.
- In the Header key field, enter the relevant value: X-Admin-User
- Select Contains as a match criteria.
- Provide Token as a header value.
- Indicate API Admin User : Requests from these users will reach any API endpoint. In the current rule example, choose this tag.
- Indicate API Privileged User : Requests from these users will reach privileged endpoints.
Step 3 (optional). Configure additional API protection settings
Additonally, you can configure the following security settings for your APIs.Auth token protection
As an additional API protection measure, you can tag the following OAuth endpoints: oauth/token, oauth2/token, and oauth2/v1/token. Protecting authentication token endpoints helps you secure APIs against unauthorized access, token theft, or brute force attacks. Our heuristic mechanism automatically detects and protects Auth token endpoints. For additional customization, you can manually tag Auth endpoints via custom rules. This will help our system apply more rigorous monitoring and protection in response to such events as multiple failed login attempts, requests with unauthorized tokens, and multiple requests to forbidden paths. To tag the endpoints, create the following custom rule: 1. Navigate to the WAAP Rules page and click Add a custom rule. 2. Give your rule a name. 3. (Optional) Add a description to provide more context about the rule. 4. In the IF section, select URL. 5. In the next dropdown, select - to apply the rule only to the specified condition. 6. Define match criteria. Select Equals to apply the rule when the URL exactly matches the specified one. 7. Enter the relevant endpoint. 8. In the THEN section, select the Tag action to apply a relevant tag to each request that matches the specified criteria. 9. In the next dropdown, select Auth Endpoint reserved tag.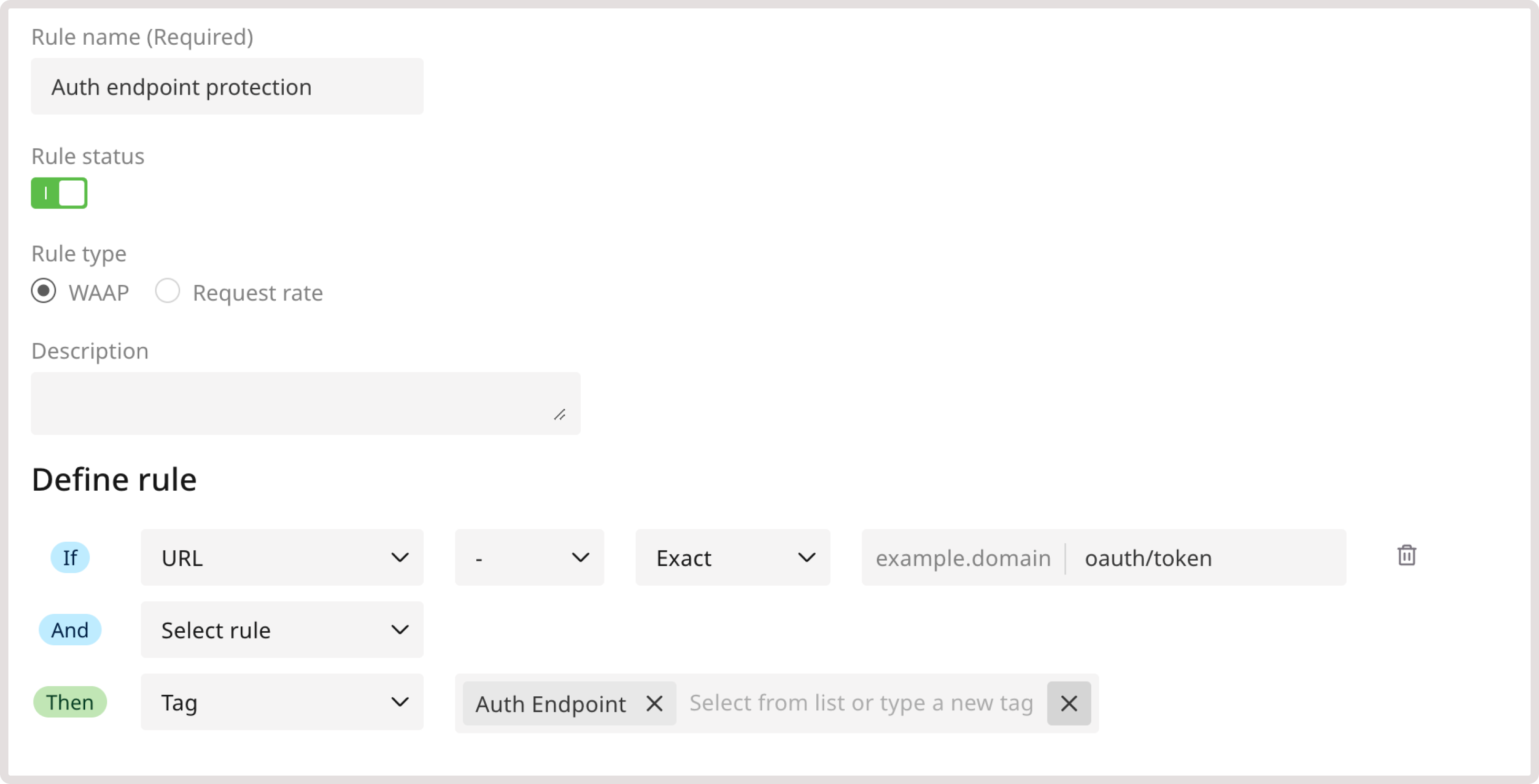
Ignore sensitive data exposure detection
You can notify the WAAP of any legitimate exposure of personally identifiable information (PII) in a request’s response, such as social security numbers, credit card numbers, emails, and phone numbers. You can also exclude the request from being affected by the sensitive data exposure policy, which encompasses broader sensitive data exposures like confidential organizational data or code leaks. Check our WAF and OWASP top threats policy group for details. This means that you can still benefit from the protection of sensitive data leakage while allowing legitimate resources to collect user information without being interrupted by WAAP. Setting up rules to ignore sensitive data can also prevent false positives and ensure that WAAP doesn’t interrupt requests to certain endpoints. For instance, create the following rule to ignore data collection during the checkout process: 1. Navigate to the WAAP Rules page and click Add a custom rule. 2. Give your rule a name. 3. (Optional) Add a description to provide more context about the rule. 4. In the IF section, select URL. 5. In the next dropdown, select - to apply the rule only to the specified condition. 6. Define match criteria. Select Contains to apply the rule when the URL partially matches the specified one. 7. Enter the relevant endpoint. In this example, /url/order/checkout. 8. In the THEN section, select the Tag action to apply a relevant tag to each request that matches the specified criteria. 9. In the next dropdown, select the Ignore Phone Number Detection and Ignore Email Address Detection tags.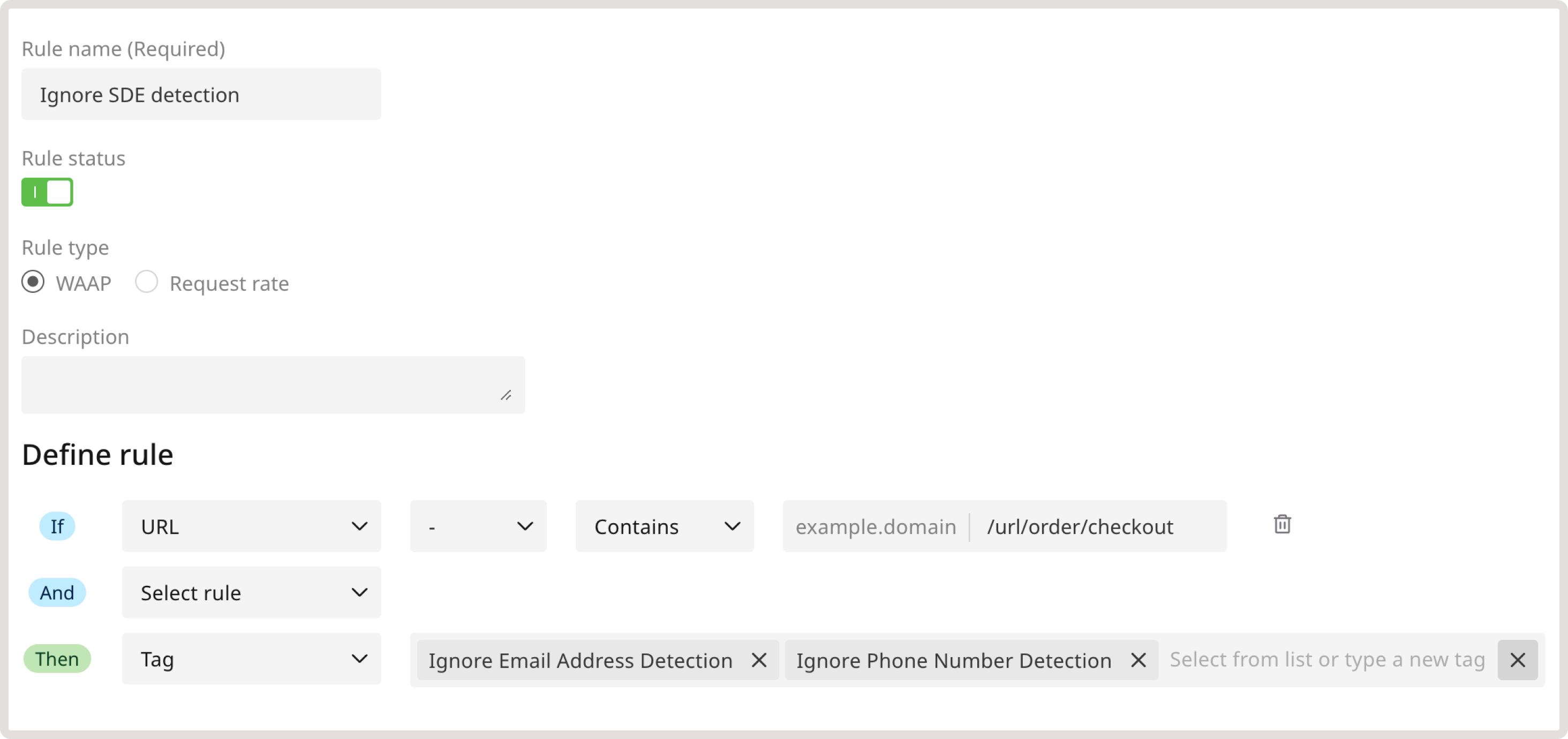
Step 4. Enable advanced API protection
After you add access tags to restricted API endpoints and configure user roles, enable the relevant Advanced API protection policies.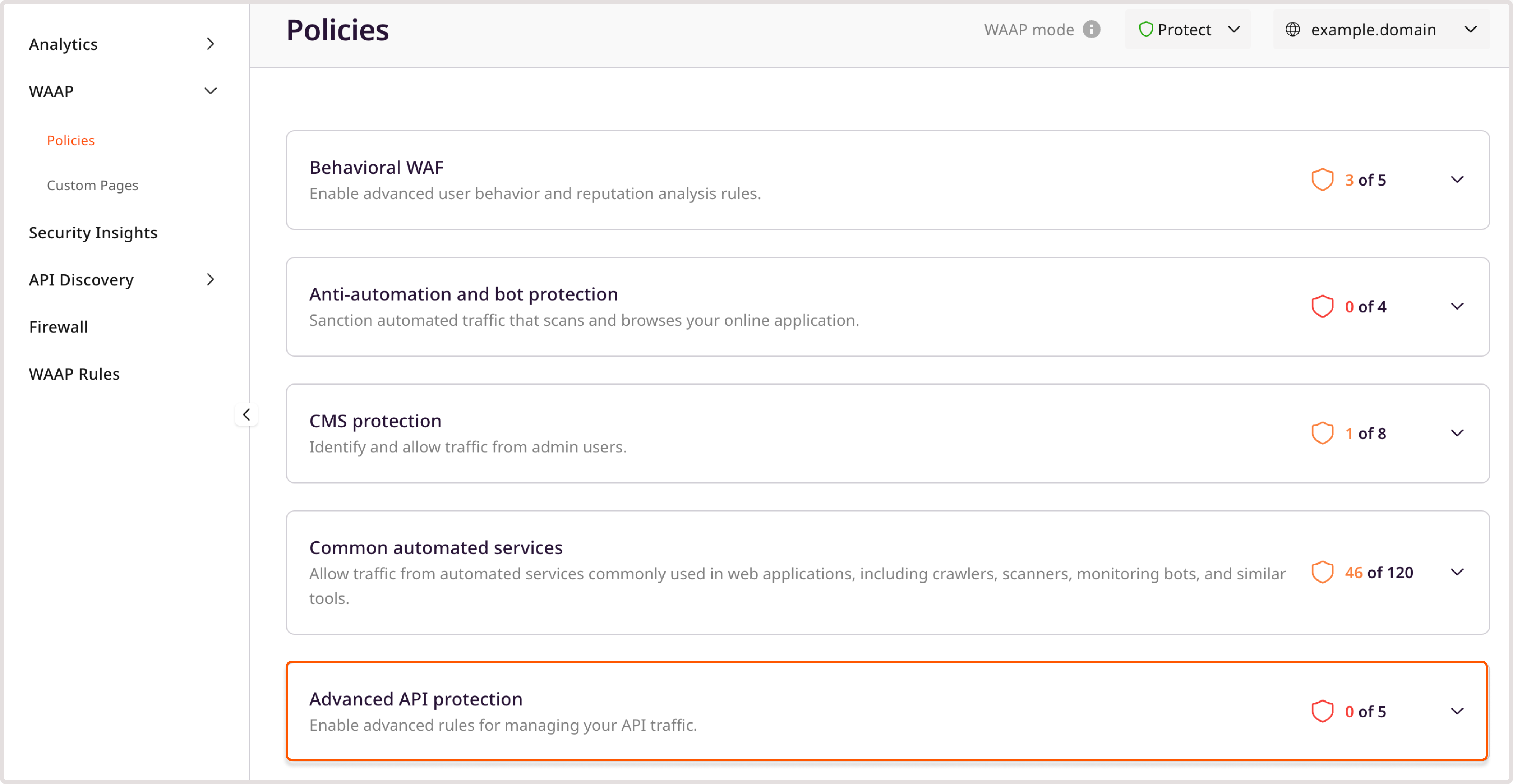
InfoAdmin users can access any endpoint, so it’s important to define users with admin roles.

