- Log in to your server.
- Navigate to the SSH directory using the following command:
- Open the SSH configuration file with root privileges using this command:
- Find the Port line in the open file and replace the value 22 with the port number you want to use. Also, remove the # symbol if it is present before the Port line.
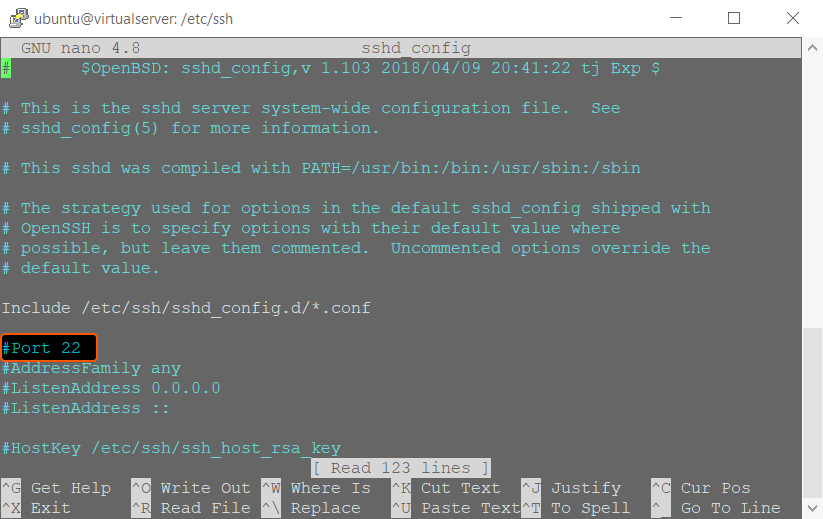
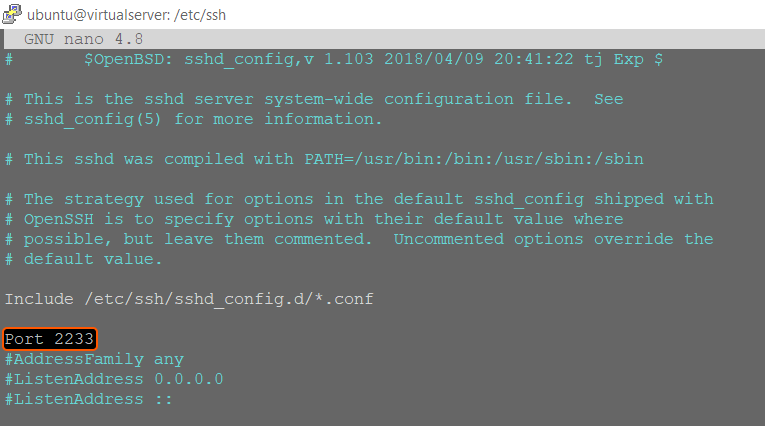
- Press Ctrl+O to save the changes.
- Restart the SSH service. For Ubuntu, Debian, or CentOS, use the following command:
- Add a rule to permit traffic exchange on the new port using the command:
- Verify if everything is functioning properly by using the command:
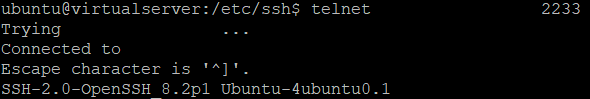
- Attempt to establish a connection to your server using the new port in a separate window without closing your current session. This step is crucial to prevent any potential loss of access to your server. If you encounter difficulties connecting to your server through the new port, revert the port back to 22 and then try again.

