TipIf you want to modify your cache key via API, refer to our API documentation.
Update cache key in CDN resource settings
You can modify the structure of your cache key by adjusting variables that capture essential request information, such as URI or the value of the Host header.InfoConsider that enabling and updating the Cache key modification feature can invalidate your current cache and affect the cache hit ratio. Furthermore, the Purge by pattern functionality won’t work.
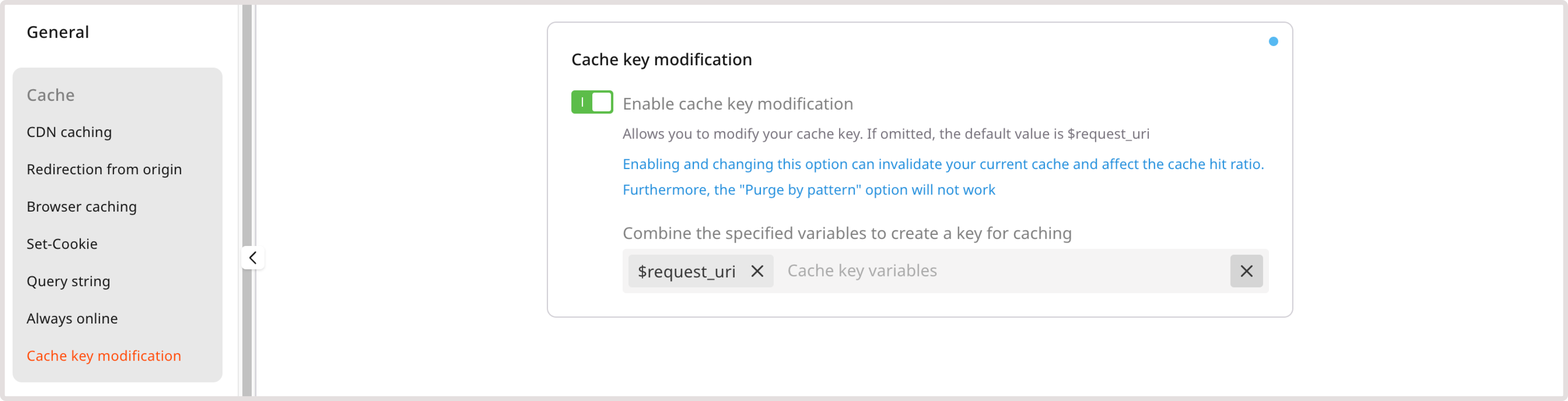
Supported variables
You can use the following variable to modify your resource’s cache key:$request_uri: The full original request URI. If used with the rewrite feature in conjunction with this option, this variable retains the value of the original URI, not the rewritten one.$scheme: The protocol used in the request.$uri: The current normalized URI in the request. The value of this variable may change during request processing. For example, it’ll change during internal redirects or when using index files.
Best practices and considerations
When configuring a cache key, take into account the following aspects to ensure optimal cache behavior:-
Using both
$uriand$request_uricache keys simultaneously will result in the cache following the$request_urikey—query strings won’t be ignored because$request_uriincludes the query string. -
The
$schemecache key does not work correctly when the Redirect HTTP to HTTPS option is enabled. All requests will be redirected to HTTPS, with no cache under the$schemekey. -
Using the
$uricache key overrides the Ignore query string option. - Cache keys restricted or added by administrators can’t be modified by the client. You can only select from the available options or contact support to request changes to such keys.
-
When you use modified cache keys, prefetch may not cover all possible cache cases. For instance, if your cache key includes both the
$request_methodand$uri, prefetching will result in warm-only HEAD requests. GET requests won’t be preloaded into the cache.

