How it works
Our listeners support Server Name Indication (SNI) extension to handle multiple TLS certificates. Based on the SNI information provided by the client, the listener selects the appropriate TLS certificate for encrypting the connection. Once the TLS connection is terminated at the listener, the Load Balancer inspects the decrypted traffic and routes it to the proper server. Each listener can also be configured with its own TLS certificate, corresponding to a specific hostname or domain.Add multiple certificates
You can add multiple certificates to listeners that use the Terminated HTTPS and Prometheus protocols.1. Add certificates to the Secrets Manager
To get started, you need to add the required certificates to Gcore Secrets Manager. If you don’t have any certificates created, To get started, you need to add the required certificates to Gcore Secrets Manager. If you don’t have any certificates created, follow the instructions from our guide on configuring secrets for HTTPS Load Balancers.2. Add certificates to a listener
After you configure the certificates, you need to add them to the relevant listener. This can be done during Load Balancer creation or in the settings of an existing Load Balancer.InfoYou can’t delete a secret that’s being used by a Load Balancer’s listener. This restriction is necessary to ensure that a Load Balancer can failover successfully when needed. In such cases, you first need to delete a listener that uses the secret and then remove the secret, recreating a listener if needed.
Create a new Load Balancer according to the instructions. In step 5, configure a new listener as follows:1. Give your listener a name.2. Select a protocol with the supported TLS encryption: Terminated HTTPS or Prometheus.3. Use a default port or specify a custom port from 1 to 65535.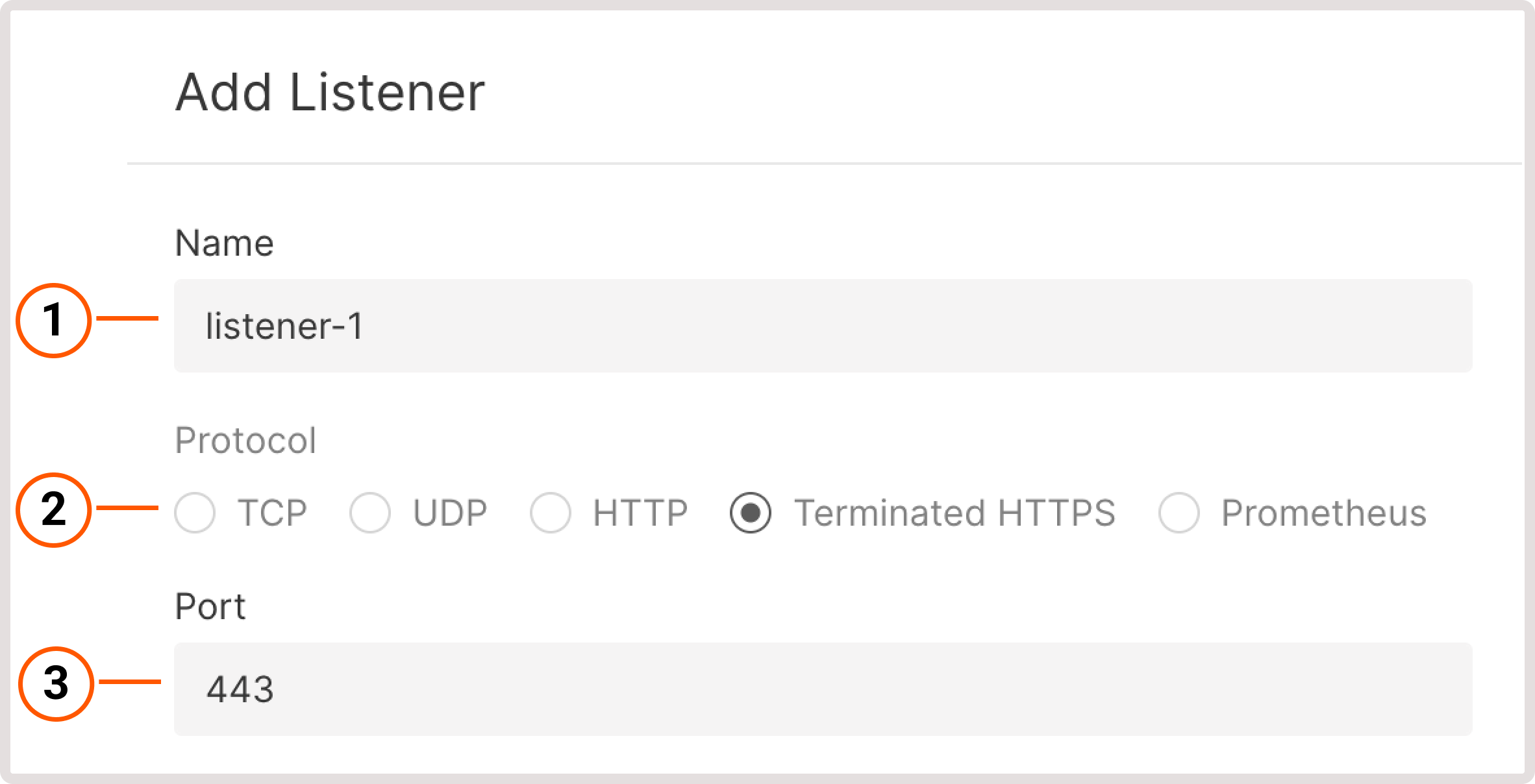 4. (Optional) To identify the origin of the user’s IP address connecting to a web server via a Load balancer, enable the Add headers X-Forwarded-For, X-Forwarded-Port, X-Forwarded-Proto to requests toggle.5. Choose the default TLS Certificate. It’s the main certificate that will be used when there’s no configured certificate for a domain.6. Select the CNI Certificates stored in the Secret Manager.7. Set the connection limit - a maximum number of simultaneous connections that can be handled by the listener.
4. (Optional) To identify the origin of the user’s IP address connecting to a web server via a Load balancer, enable the Add headers X-Forwarded-For, X-Forwarded-Port, X-Forwarded-Proto to requests toggle.5. Choose the default TLS Certificate. It’s the main certificate that will be used when there’s no configured certificate for a domain.6. Select the CNI Certificates stored in the Secret Manager.7. Set the connection limit - a maximum number of simultaneous connections that can be handled by the listener.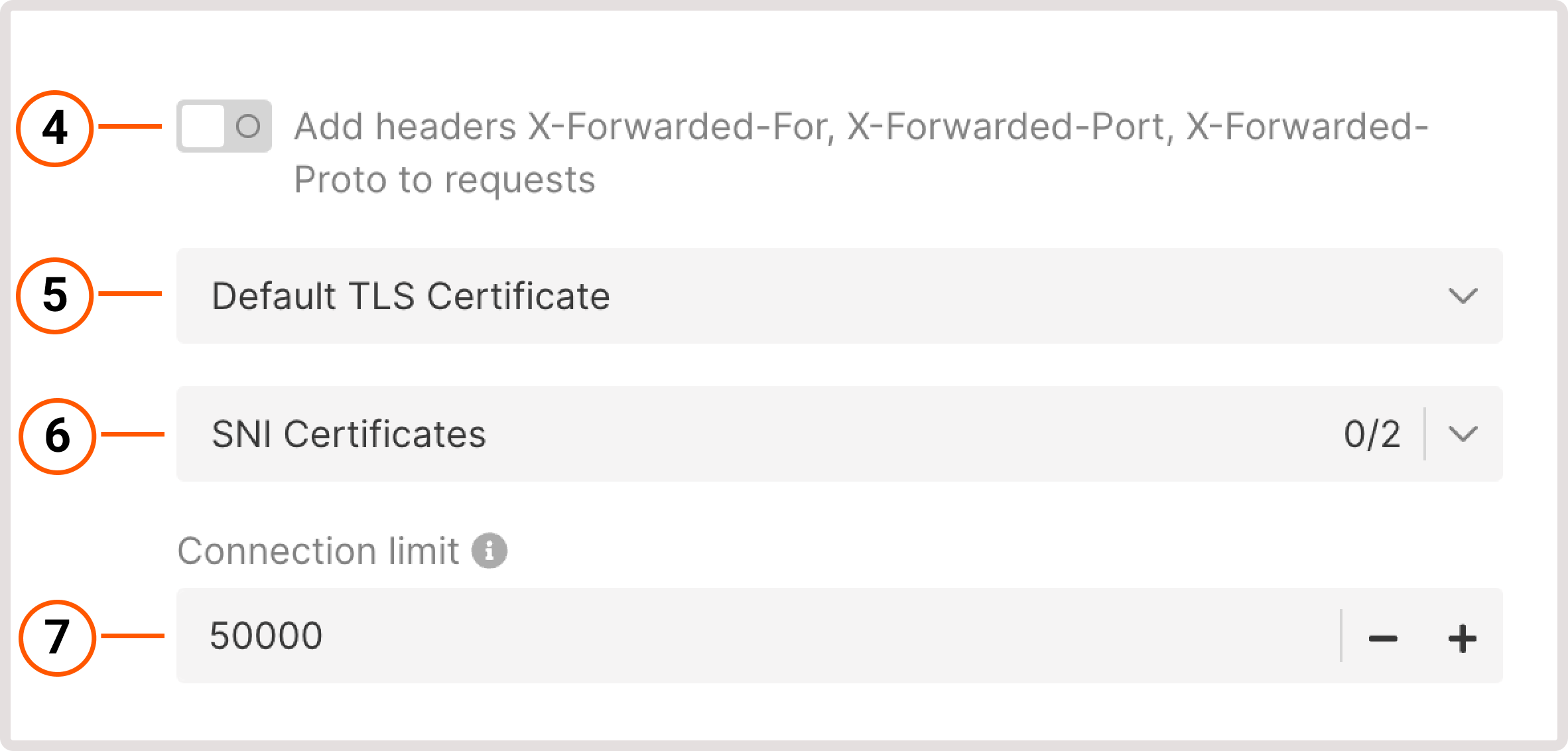 8. (Optional) Add allowed CIDR ranges to define which IP addresses can access your content. All IP addresses that don’t belong to the specified range will be denied access.9. (Optional) Configure Basic Authentication for HTTP traffic to protect your resource from unauthorized access. Click Add user to specify who can access your resource only by logging in with the following credentials:
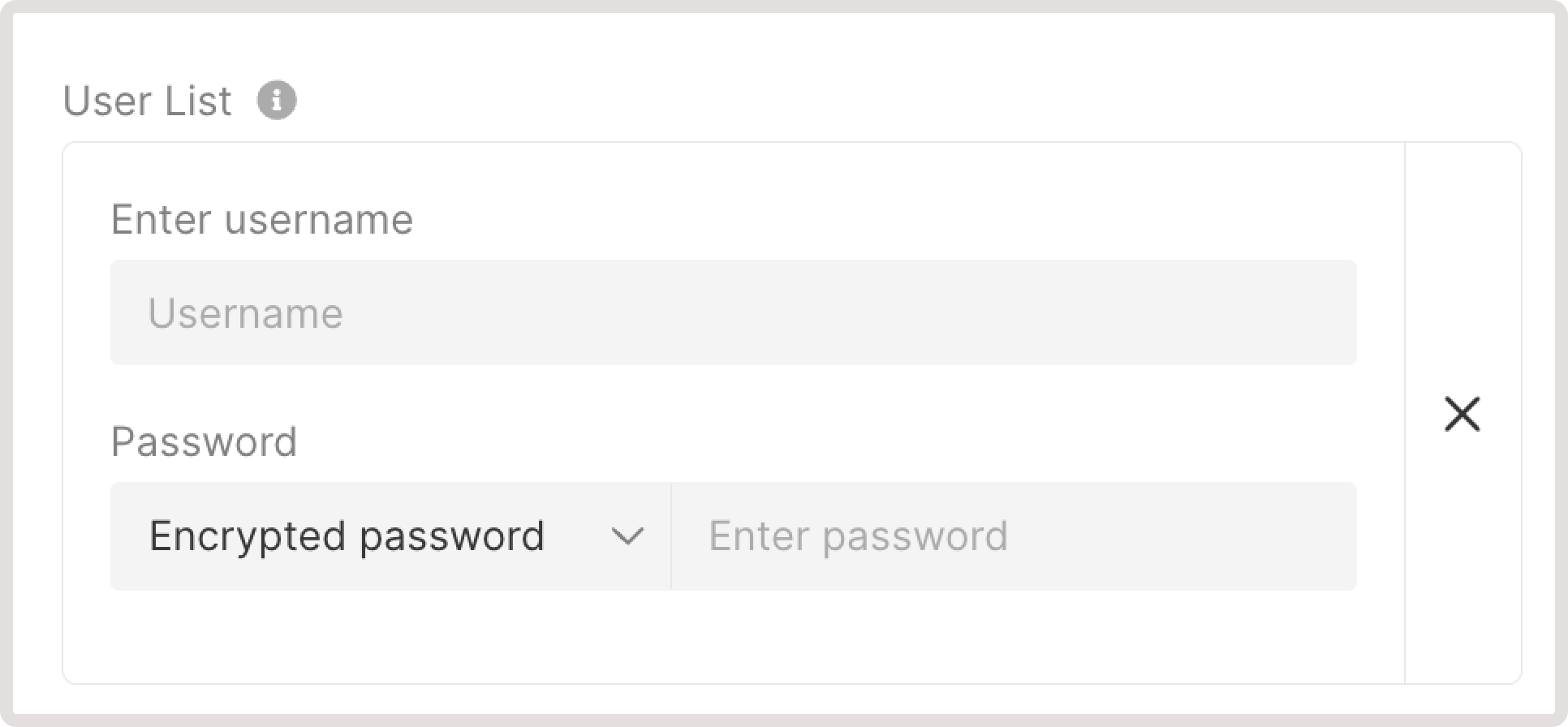
8. (Optional) Add allowed CIDR ranges to define which IP addresses can access your content. All IP addresses that don’t belong to the specified range will be denied access.9. (Optional) Configure Basic Authentication for HTTP traffic to protect your resource from unauthorized access. Click Add user to specify who can access your resource only by logging in with the following credentials: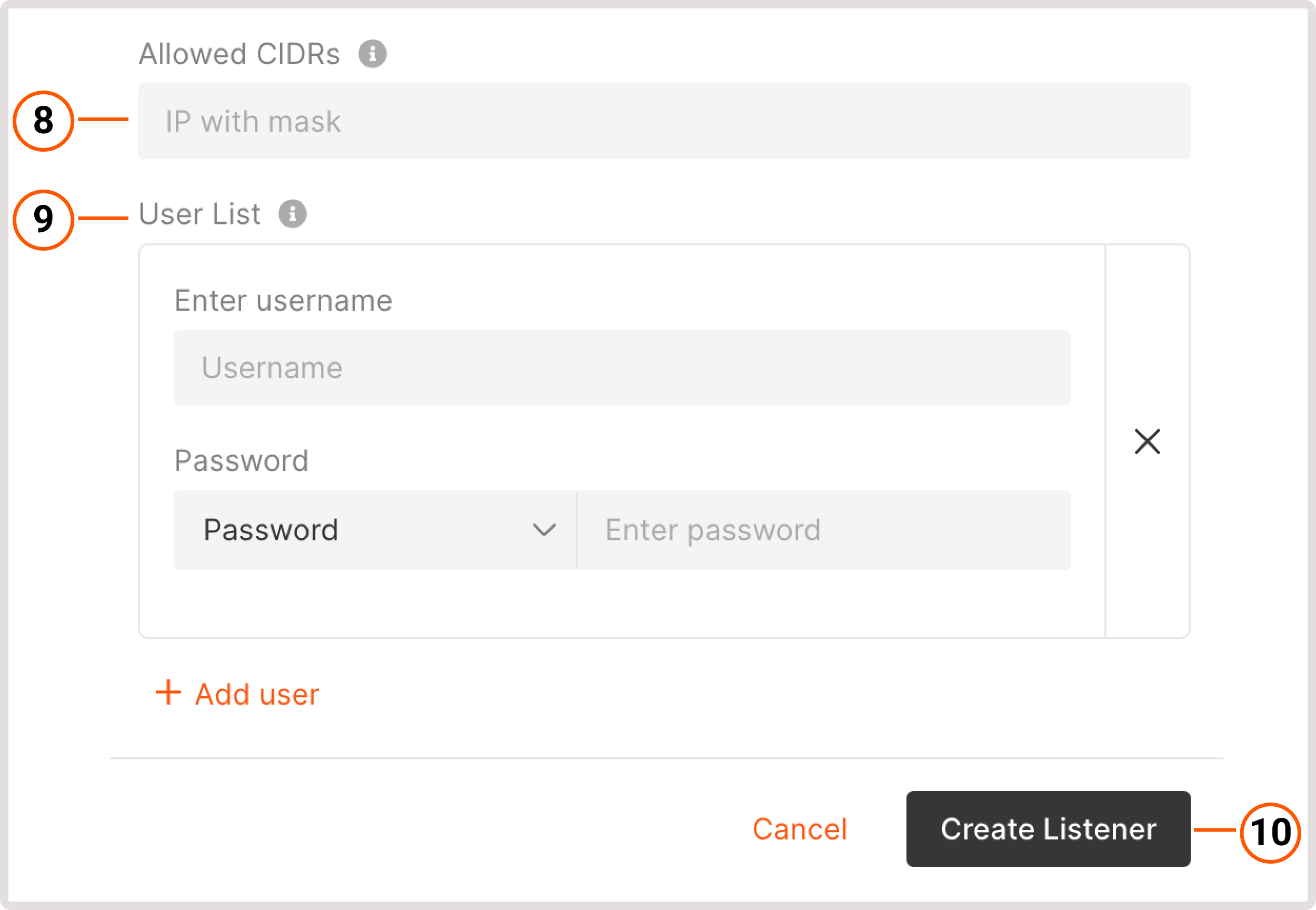


- Enter username : specify a username that needs to be entered on the login screen.
- Password : specify a password or provide an encrypted password.

Create an encrypted password
When configuring basic authentication for HTTP traffic, you have the option to specify an encrypted password for a user. You can use any preferred encryption method or generate a hashed password using the MKPasswd utility. To generate a password hash using a dockerized version of MKPasswd: 1. Check the available encryption types: